このほど、東京大学先端科学研究センター(東京都目黒区駒場、中野義昭所長)システム生物医学分野の三村維真理(みむら いまり)研究員(現、東京大学腎臓内分泌内科)と児玉龍彦教授、和田洋一郎特任准教授らの研究グループは転写因子HIF1A (Hypoxia inducible factor 1 alpha)が血管内皮細胞において低酸素環境でヒストン修飾酵素と協調的に下流の遺伝子発現を制御することを明らかにした。本内容は2012年5月29日付でMolecular and Cellular Biology (American society for microbiology)電子版に掲載された。
転写因子HIF1Aは低酸素下においてDNAに結合して遺伝子の発現、細胞の性質を制御することが知られている。HIF1Aは正常酸素分圧下ではプロリルハイドロキシラーゼ(PHD: prolyl hydroxylase)により水酸化された後、ユビキチン化を受けて分解されるが、低酸素分圧下ではPHDが働けなくなるため分解をまぬかれてその機能を発揮する。近年、低酸素下においてjumonji-domainを含む一連のヒストン脱メチル化酵素群の発現が誘導されること、その一部はHIF1Aによって転写調節を受けることが報告されている。しかし、低酸素下における転写因子とヒストン脱メチル化酵素の間の相互作用については不明であった。そこで、今回は低酸素刺激によって内皮細胞で高度に誘導されるヒストン脱メチル化酵素であるKDM3Aに着目して、HIF1Aとの関係を検討した。
まず、クロマチン免疫沈降と超高速シーケンサー(ChIP-Seq)を用いて、HIF1Aの結合部位を全ゲノム上で明らかにした(図1)。また、ヒストン脱メチル化酵素KDM3AとHIF1Aのノックダウンによるアレイ解析からその下流遺伝子群を同定した(図2)。
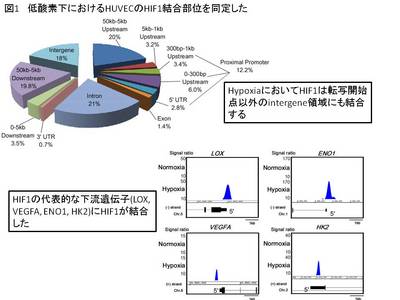
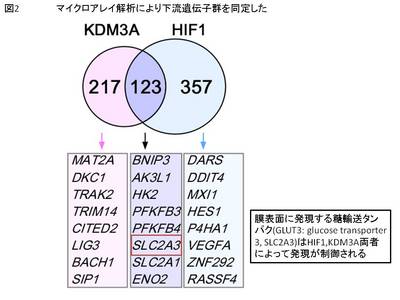
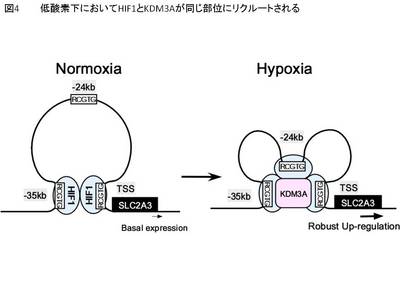
次に、HIF1AおよびKDM3A両者によって発現が制御される標的遺伝子SLC2A3(Solute carrier family2A3: GLUT3; glucose transporter 3)に着目した。SLC2A3はノックダウンすると低酸素下においてHUVECのtube formationおよび細胞内へのグルコースの取り込みが阻害されることから血管内皮細胞の維持において重要な役割を果たす遺伝子である。ChIP-seqによって低酸素下でSLC2A3遺伝子の転写開始点およびエンハンサー領域2か所の計3か所にHIF1Aが結合することが明らかとなったが、これら3か所が生体内のクロマチン構造上では立体的に近接していることをChromatin conformation capture(3C)法によって示した(図3)。
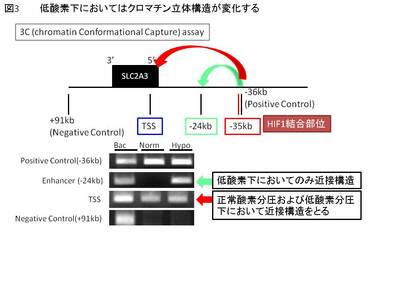
上記で示された低酸素下におけるクロマチン立体構造の変化において、ヒストン修飾酵素であるKDM3Aの挙動を解析した。その結果、KDM3AはSLC2A3のHIF1A依存的にHIF1A結合部位と同じ場所にリクルートされており、その時HIF1AとKDM3Aは免疫沈降産物に共存していた。以上の結果に基づいて、今回の論文では低酸素下におけるHIF1AとKDM3Aによるクロマチン立体構造変化を含む新規の転写制御機構を見出したことを報告した(図4)。
本研究は、システム生物医学ラボラトリーのゲノムサイエンス部門、代謝医学部門、及び分子生物医学部門との共同作業、並びに大阪大学木村宏博士との協力によって実施された。
Dynamic change of the chromatin conformation in response to hypoxia enhances the expression of GLUT3 (SLC2A3) by cooperative interaction of HIF1 and KDM3A.
Mimura I, Nangaku M, Kanki Y, Tsutsumi S, Inoue T, Kohro T, Yamamoto S, Fujita T, Shimamura T, Suehiro JI, Taguchi A, Kobayashi M, Tanimura K, Inagaki T, Tanaka T, Hamakubo T, Sakai J, Aburatani H, Kodama T, Wada Y.
Mol Cell Biol. 2012 May 29. [Epub ahead of print]




